Understanding Executive Schedule Pay vs. SES Pay (for Federal Job Seekers)

The following post explores Understanding Executive Schedule Pay vs. SES Pay (for Federal Job Seekers).
For many federal job seekers aiming for senior leadership positions, the difference between Executive Schedule pay and Senior Executive Service (SES) pay can be confusing.
Read: Understanding the SES Qualifications Review Board (for Federal Job Seekers)
Related: Navigating Major SES Changes
Both involve high-level roles, but the way salaries are determined is very different. Understanding these distinctions can help applicants set expectations and better navigate their career paths.
Here’s what you need to know.
Executive Schedule (EX) Pay
What is Executive Schedule (EX) pay in the federal government?
Simply put, it’s a fixed, statutory salary structure for certain leadership positions in the federal government including agency heads, Cabinet secretaries, and other high-level political appointees.
The key thing to understand about Executive Schedule pay is that it is set by law. Salaries for each level are fixed and do not change based on individual performance, agency, or other factors.
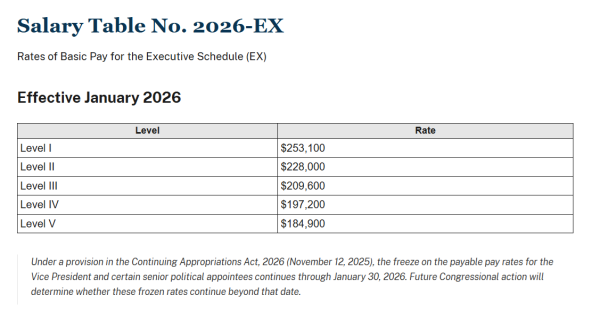
Essentially, if a position is classified at a specific Executive Schedule level, you know exactly what the salary will be. Positions are classified into five levels (I–V), with Level I representing the highest pay.
Executive Schedule Pay – Example
Jane has been appointed as the head of a federal agency, a position classified at Executive Schedule Level II. For 2026, Level II pays $203,700. Because her pay is statutory, Jane receives exactly $203,700, regardless of her performance or agency-specific factors. Everyone else in Level II receives the same fixed salary.
Below is a screenshot of the Executive Schedule salary table for 2026.
Senior Executive Service (SES) Pay
What is Senior Executive Service (SES) pay in the federal government?
Unlike Executive Schedule pay, SES pay is not a single fixed salary. Instead, it operates within a pay range that allows agencies flexibility to set individual compensation for career senior executives.
The most important thing to understand about SES pay is that it is performance-based. This means two SES executives in similar roles can earn different salaries depending on their performance.
In practical terms, SES pay works more like a band than a ladder. There is a minimum and a maximum rate of basic pay, and agencies place executives somewhere within that band.
SES Pay – Example
John is a career SES executive at the same agency. The SES pay range for his position is $170,000–$215,000. His agency determines his salary based on performance. If John demonstrates outstanding results, he might earn $210,000. If his performance is average, he could earn $180,000. Another SES colleague might earn a different amount, even in the same role, because SES pay is flexible within the pay band.
Below is a screenshot of the SES basic pay range table for 2026.

In Conclusion
In conclusion, I hope this article is helpful for understanding the difference between Executive Schedule and SES pay. Executive Schedule pay is fixed by law and applies to appointed leadership roles. SES pay is performance-based within a set range. Understanding the difference will help applicants set realistic expectations and understand how performance can influence their compensation as an SES member.
If you’re ready for professional assistance with building your new two-page Federal Resume, my team and I are here to support you. Please use the Contact Us or Submit Your Resume for a risk-free evaluation. JobStars is an A+ BBB-rated service that has earned multiple consecutive Complaint Free Awards.








